Overview
Scoliosis is the deformity of the spine. It presents itself as deformed curvature of the spine forming an S or a C curve, measuring 10 degrees or more.
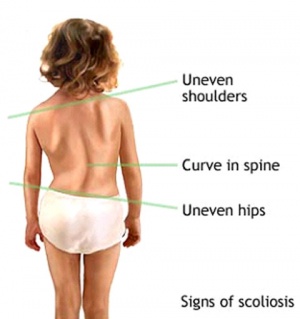
The child may appear to be leaning to one side. Both the middle (thoracic) and lower (lumbar) spine may be affected.
Causes
In most cases, the cause scoliosis is not known. A child may be born with it or can develop it later in life. It’s most often observed in children between the ages of 10 and 18 and it tends to affect girls more than boys.
Possible causes of scoliosis include:
- cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy
- Inherited conditions that tend to run in families
- Leg length discrepancy
- Injury
- Infection
- Tumors
Clinical Assessment
Symptoms can occur differently and in varied degrees in each child. Following are some symptoms that can be looked out for:
- Difference in shoulder height
- The head not centred with the rest of the body
- Pelvic misalignment
- Difference in shoulder blades height or position
- Difference in the way the arms hang beside the body when the child stands straight
- Difference in the ribcage appearance when the child bends forward
Diagnosis
Your child’s healthcare provider or physical therapist may require the following tests to understand the degree of scoliosis in the child:
- X-rays: It is the primary tool for diagnosing scoliosis. It measures the degree of spinal curvature.
- MRI: This test constructs detailed images of organs and structures within the body to determine soft tissue damages if any
- CT scan: This test uses X-rays make detailed images of the body to understand the degree of the scoliosis and any bone damages or tumors if any.
An early diagnosis is important for treatment. If left untreated, scoliosis can cause problems with heart and lung function.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the child’s symptoms, age, and general health and of course, the severity of the problem.
The goal of treatment is to stop the worsening of the curve and prevent severe deformity. Treatment may include:
- Bracing: If your child is still growing, he or she may need a brace for some time.
- Assessment and Physical therapy: In addition to bracing the child will also require strengthening exercise regimen to strengthen his/her muscles in order to sustain the correction achieved with bracing and manual manipulation.
- Surgery: Your child may need surgery if the curve measures 45 degrees or more on an X-ray and bracing has no effect on the progression of the curve.
- Exercise Regimen and Maintenance: Even after surgery and or bracing the child will have to maintain a disciplined routine of exercises to maintain the correction and overall muscular and core strength in order to lead a normal and active life. The child and the parents must closely work with a physiotherapist to create a holistic exercise regimen for the same.
For more details please contact us or visit our www.phyworld.in